Styled GeoJSON
Tutorial by Ranen Ghosh
This tutorial will show you how to add GeoJSON files to the map or globe. The features in the GeoJSON files will have their colors and other display properties set by a separate Styled Layer Descriptor document.
Getting started
You will need to have already run through the remote image layer tutorial. Let’s get started by opening your HelloEarth project.
If you haven’t got one here is a suitable ViewController file to start with (for Objective-C or Swift). This version is from the previous tutorial for a remote image layer.
Get some data
At this time, download some GeoJSON data to play with. We’re going to use the Belfast dataset from Mapzen’s Metro Extracts. Download this file and extract it into your working directory:
https://s3.amazonaws.com/metro-extracts.mapzen.com/belfast_ireland.imposm-geojson.zip
Drag the files belfast_ireland_landusages.geojson, belfast_ireland_buildings.geojson, and belfast_ireland_roads.geojson into your project.
We’re also going to need some Styled Layer Descriptor stylesheets. Here are one for each layer: landuse.sld, buildings.sld, and roads.sld. Download those into your working directory, and drag them into your project as well.
Start up over Belfast
Change the last part of viewDidLoad so that the app starts over Belfast.
-
// start up over Belfast if (globeViewC != nil) { globeViewC.height = 0.8; [globeViewC animateToPosition:MaplyCoordinateMakeWithDegrees(-5.93,54.597) time:1.0]; } else { mapViewC.height = 1.0; [mapViewC animateToPosition:MaplyCoordinateMakeWithDegrees(-5.93,54.597) time:1.0]; } -
// start up over Belfast if let globeViewC = globeViewC { globeViewC.height = 0.8 globeViewC.animate(toPosition: MaplyCoordinateMakeWithDegrees(-5.93,54.597), time: 1.0) } else if let mapViewC = mapViewC { mapViewC.height = 1.0 mapViewC.animate(toPosition:MaplyCoordinateMakeWithDegrees(-5.93,54.597), time: 1.0) }
The GeoJSONSource object
The GeoJSONSource object allows you to add, remove, enable disable GeoJSON vector features on the globe or map.
If you’re using Objective-C, then include the header in your ViewController.m source file.
-
#import "GeoJSONSource.h"
Add some GeoJSONSource objects for land use, buildings, and roads to your ViewController’s member variables:
-
GeoJSONSource *landUseSource, *buildingsSource, *roadsSource; -
fileprivate var landUseSource: GeoJSONSource? fileprivate var buildingsSource: GeoJSONSource? fileprivate var roadsSource: GeoJSONSource?
Starting with land use
We’re going to first display the land use GeoJSON file on the globe/map. To do this, we construct the GeoJSONSource object, passing in the map/globe view controller and URLs for both the GeoJSON and SLD files. There’s also a relativeDrawPriority argument, to control the order of different layers. The only catch is that we have to give the map/globe a chance to set up first; for this reason we’ll construct the GeoJSONSource object after a short delay (using dispatch_after in Objective-C, or asyncAfter in swift):
-
dispatch_after( dispatch_time(DISPATCH_TIME_NOW, 1.0 * NSEC_PER_SEC), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ landUseSource = [[GeoJSONSource alloc] initWithViewC:theViewC GeoJSONURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"belfast_ireland_landusages" withExtension:@"geojson"] sldURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"landuse" withExtension:@"sld"] relativeDrawPriority:100]; [landUseSource startParse]; }); -
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 1.0) { self.landUseSource = GeoJSONSource.init(viewC: self.theViewC!, geoJSONURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "belfast_ireland_landusages", withExtension: "geojson"), sldURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "landuse", withExtension: "sld"), relativeDrawPriority:100) self.landUseSource?.startParse() }
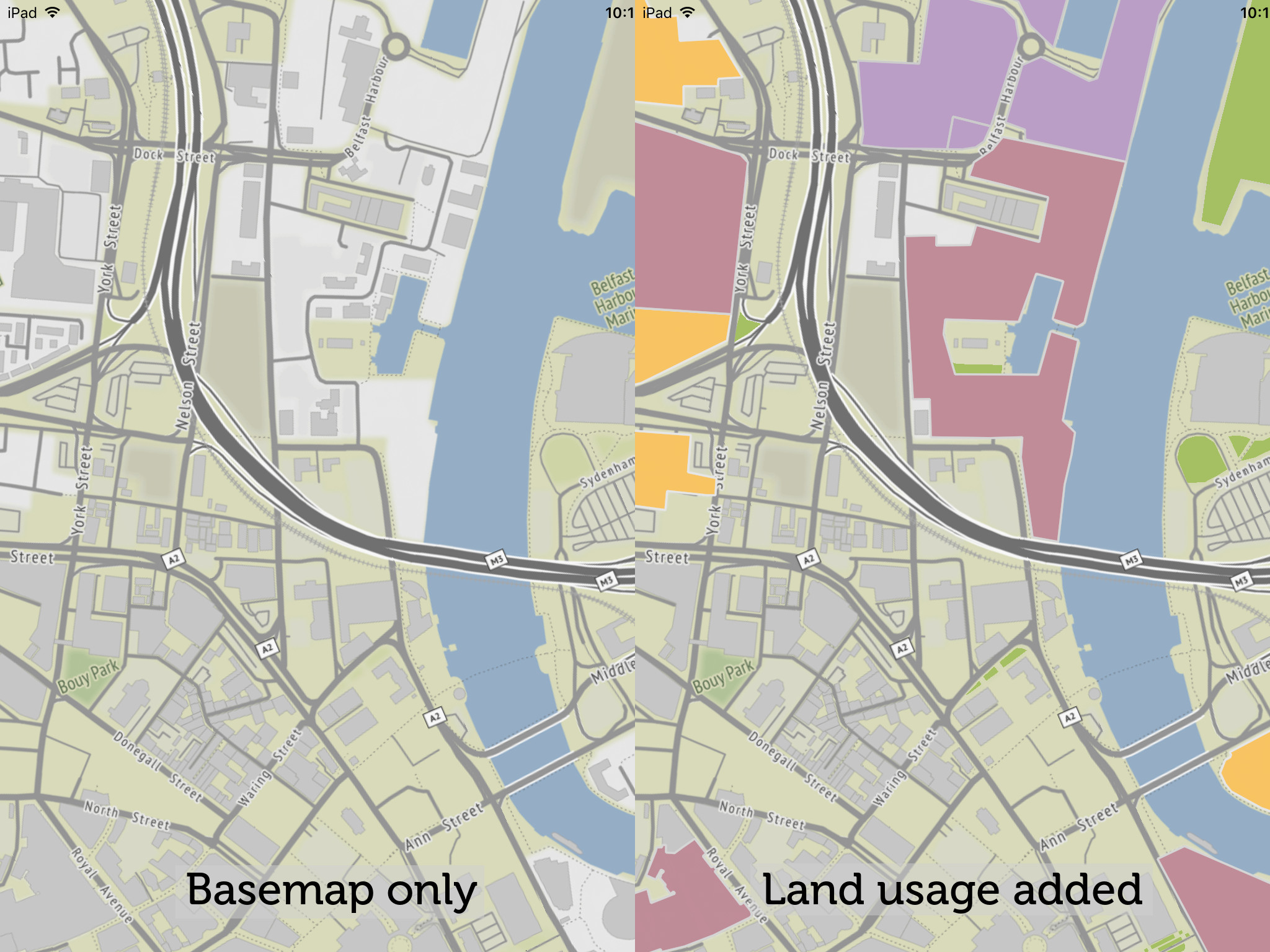
Now, when you zoom to Belfast, Northern Ireland, you’ll see the land usages overlaid on the basemap.
Adding more layers, asynchronously
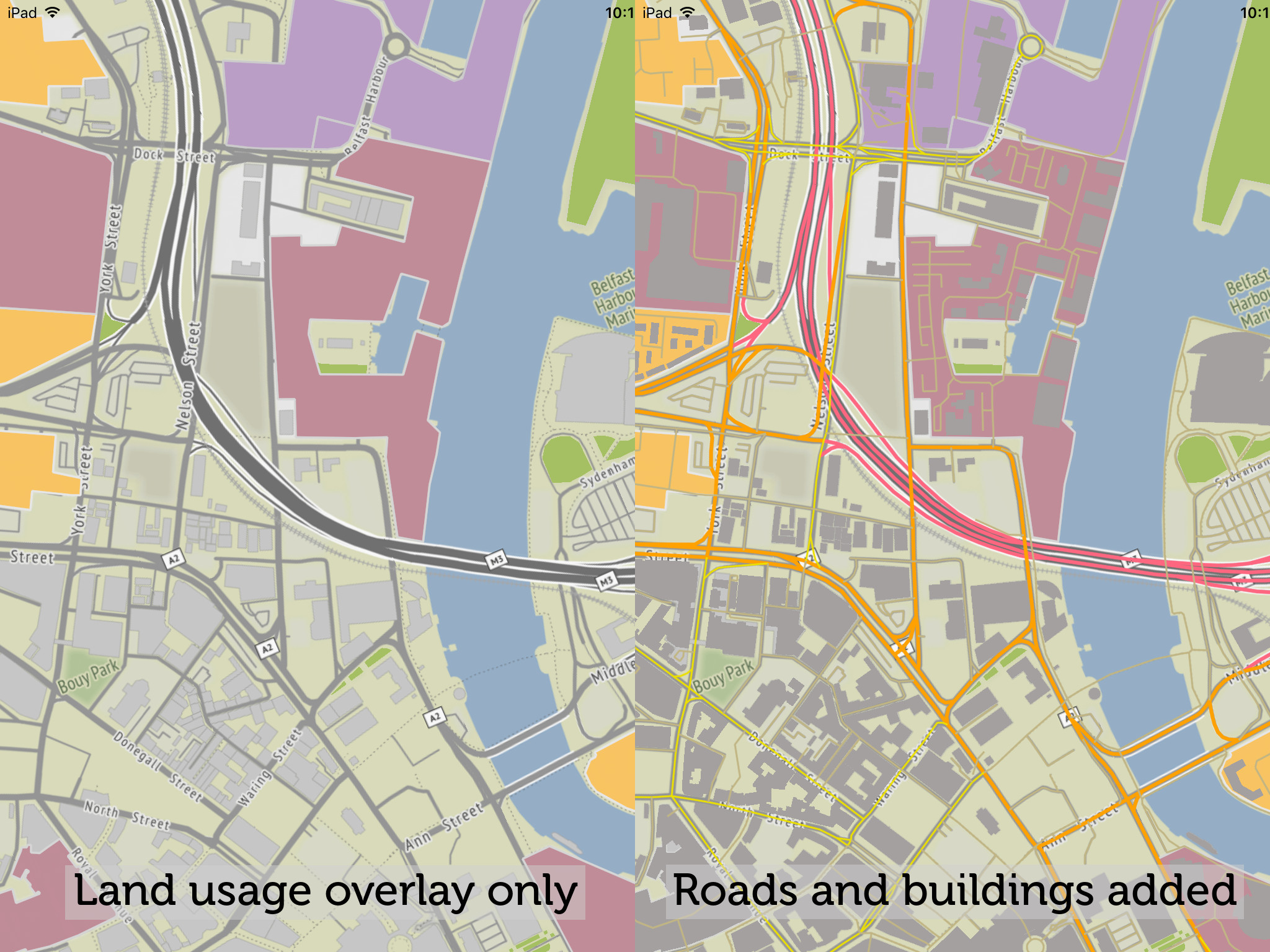
We’re going to add additional layers for buildings and roads. But to prevent the app from slowing down while loading three different data layers at once, we’re going to read the data in sequentially.
You’ll have noticed that, in the previous section, the parsing method was called startParse. This is because the method returns immediately to avoid locking up the UI thread, but the parsing will run in a background thread.
With the additional data layers to process, we’re going to use the startParseWithCompletion method, instead.
First, change the call to startParse with startParseWithCompletion:
-
[landUseSource startParseWithCompletion:^() { }]; -
self.landUseSource?.startParse(completion: { })
This simply passes in an empty code block to be run after parsing is completed. So far, there is no actual change in behavior.
Now, we’ll load a second data layer (buildings) after the first one is finished parsing. We’ll add code inside the completion block:
-
[landUseSource startParseWithCompletion:^() { buildingsSource = [[GeoJSONSource alloc] initWithViewC:theViewC GeoJSONURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"belfast_ireland_buildings" withExtension:@"geojson"] sldURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"osm_buildings" withExtension:@"sld"] relativeDrawPriority:200]; [buildingsSource startParseWithCompletion:^() { }]; }]; -
self.landUseSource?.startParse(completion: { self.buildingsSource = GeoJSONSource.init(viewC: self.theViewC!, geoJSONURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "belfast_ireland_buildings", withExtension: "geojson"), sldURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "osm_buildings", withExtension: "sld"), relativeDrawPriority:200) self.buildingsSource?.startParse(completion: { }) })
And to add the third data layer (roads), we’ll nest the third GeoJSONSource parsing inside the completion block of the second:
-
[landUseSource startParseWithCompletion:^() { buildingsSource = [[GeoJSONSource alloc] initWithViewC:theViewC GeoJSONURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"belfast_ireland_buildings" withExtension:@"geojson"] sldURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"osm_buildings" withExtension:@"sld"] relativeDrawPriority:200]; [buildingsSource startParseWithCompletion:^() { roadsSource = [[GeoJSONSource alloc] initWithViewC:theViewC GeoJSONURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"belfast_ireland_roads" withExtension:@"geojson"] sldURL:[[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"osm_roads" withExtension:@"sld"] relativeDrawPriority:300]; [roadsSource startParse]; }]; }]; -
self.landUseSource?.startParse(completion: { self.buildingsSource = GeoJSONSource.init(viewC: self.theViewC!, geoJSONURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "belfast_ireland_buildings", withExtension: "geojson"), sldURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "osm_buildings", withExtension: "sld"), relativeDrawPriority:200) self.buildingsSource?.startParse(completion: { self.roadsSource = GeoJSONSource.init(viewC: self.theViewC!, geoJSONURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "belfast_ireland_roads", withExtension: "geojson"), sldURL: Bundle.main.url(forResource: "osm_roads", withExtension: "sld"), relativeDrawPriority:300) self.roadsSource?.startParse() }) })
Other GeoJSONSource properties and methods
The GeoJSONSource object has a readonly boolean loaded property to tell you if it’s done parsing the input json file. There’s also a settable boolean enabled property (which starts as true once the json file is parsed), which can be set to false to hide the features from the map/globe. Finally, there’s a teardown method to remove the features from the globe/map, and free associated resources.